Research History
1902: John James R. Macleod, MD, conducted research that led to the discovery of insulin.
1910: Lakeside Hospital was the world’s first hospital to perfect the manufacture of nitrous oxide gas.
1917: David Marine, MD, discovered that goiter can be prevented and cured by iodine supplementation, leading to the availability of iodized salt around the country and the world.
1920: Frederick Mautz, MD, designed an artificial pulmonary ventilation machine.
1923: Henry Gerstenberger, MD, received a patent for infant formula known as SMA (Synthetic Milk Adapted), developed at Babies Dispensary and Children’s Hospital in collaboration with Harold Ruh, MD, and biochemist William Frohring.

1933: Claude Beck, MD, performed the first successful removal of a heart tumor.
1934: Harry Goldblatt, MD, described the role of the kidneys in hypertension (high blood pressure), laying the foundation for the discovery of renin and eventually the development of enzyme-inhibitor medications to treat chronic hypertension.
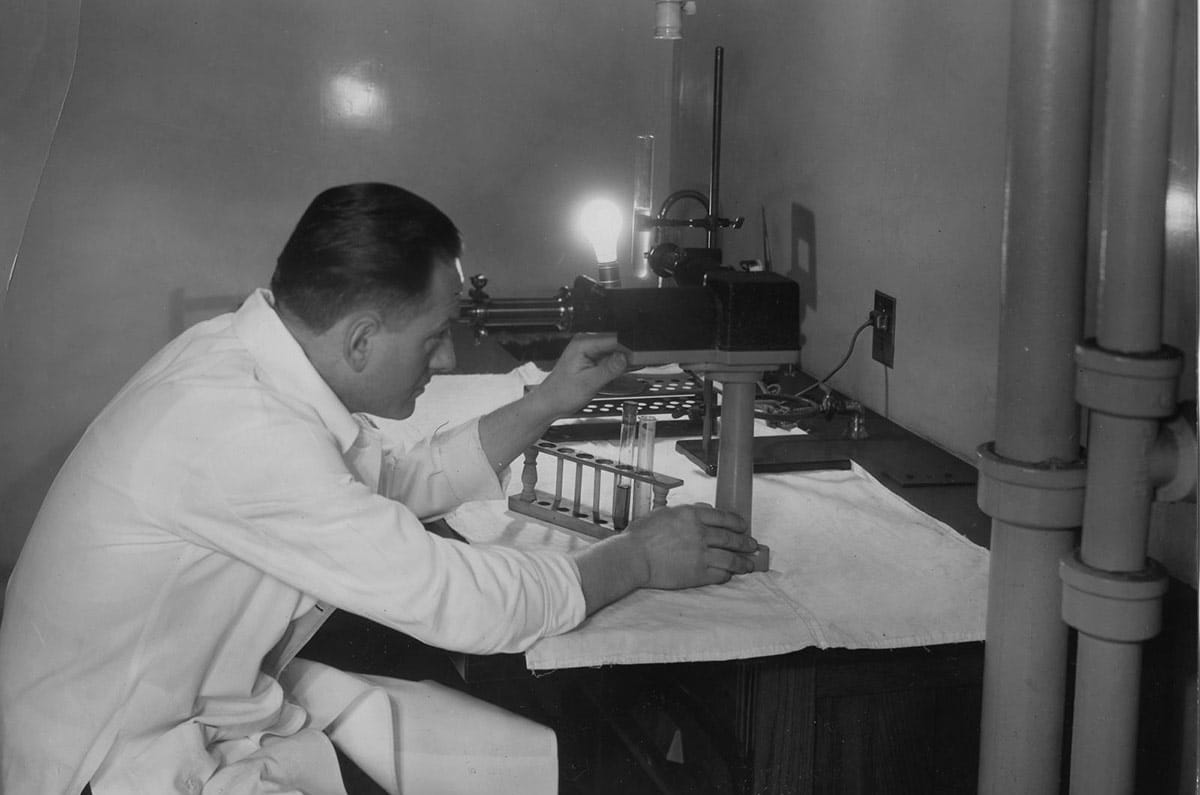

1935: Claude Beck, MD, performed the first operation for coronary artery disease.
1944: Walter Heymann, MD, began research on kidney disease in children.
1946: Louis Pillemer, PhD, developed preparations of tetanus antigen, leading to the first successful triple vaccine (DPT) targeting diphtheria, pertussis (whooping cough) and tetanus, which virtually eliminated these once-fatal diseases in the U.S.
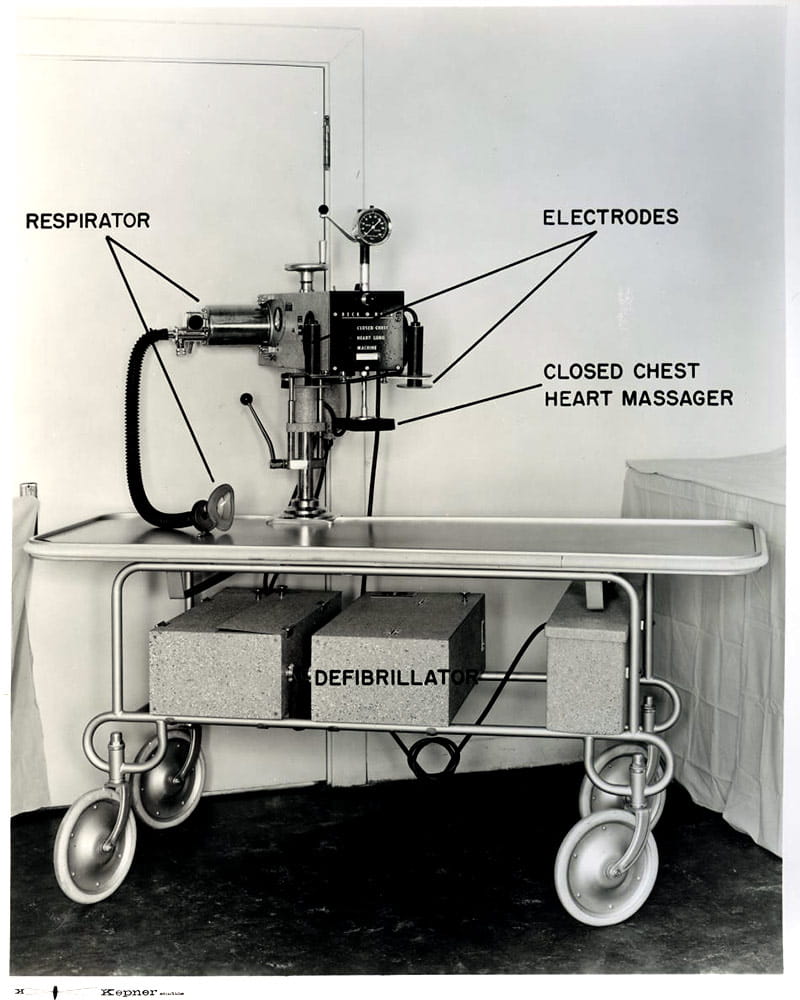
1947: Claude Beck, MD, performed the first successful defibrillation of a human heart.
1947: Hymer Friedell, MD, initiated research that became the essential source of information on the long-term effects of radiation on humans.
1951: James Reagan, MD, pioneered cytopathology for cancer detection and introduced diagnostic terminology for Pap smear results reporting, including dysplasia, carcinoma in situ and squamous carcinoma.
1952: Claude Beck, MD, helped develop cardiopulmonary resuscitation techniques and played an instrumental role in promoting their use.

1952: Use of chloramphenicol in blood disease was developed by Austin Weisberger, MD.
1953: Frank Nulsen, MD, pioneered pressure-regulated one-way valves for the treatment of hydrocephalus (water on the brain). He, along with Charles Herndon, MD, and Lester Persky, MD, also established one of the first hydrocephalus and myelodysplasia clinics for children in the country.
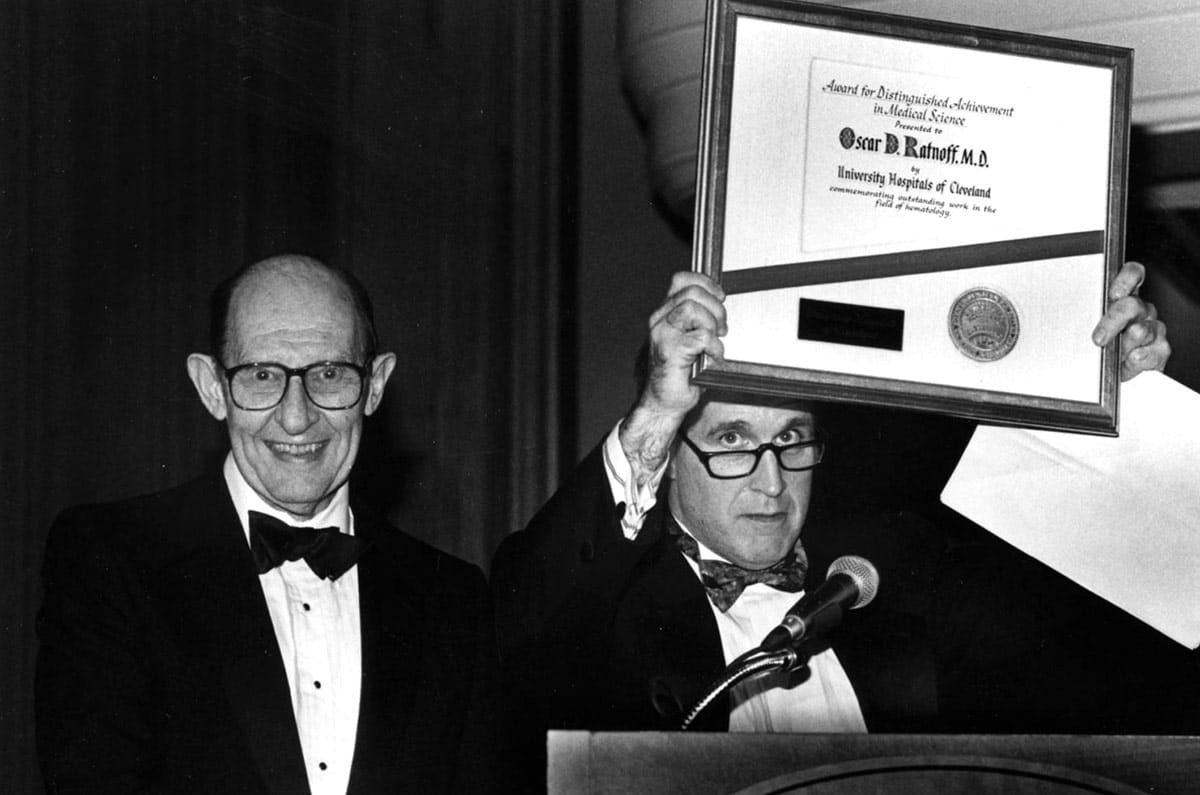
1953: Oscar Ratnoff, MD, an international expert on blood coagulation, discovered the Hageman Blood Factor. This work led to the 1975 discovery of the Fitzgerald Factor (Factor XI).

1954: Louis Pillemer, PhD, in collaboration with Irwin Lepow, PhD, and Enrique Ecker, PhD, discovered an alternative pathway for the immune response that does not involve antibodies. Drs. Ecker and Lepow also defined components of the classical pathway of complement activation, a system of proteins in the blood that is activated to initiate the immune response.
1955: Claude Beck, MD, and Walter Pritchard, MD, performed the first successful reversal of a fatal heart attack outside of an operating room, with open heart massage.
1958: Benjamin Spock, MD, launched his groundbreaking child-rearing study that explored breast-feeding, weaning, toilet training and separation anxiety while an associate physician in the Department of Psychiatry.
1961: Albert Potts, MD, PhD, receives the Association of Research in Vision and Ophthalmology Friedenwald Award for his studies of alcohol toxicity on the optic nerve, which helped advance the understanding of how the optic nerve works.
1962: Joseph T. Wearn Laboratory for Medical Research opened on the University Circle campus.
1965: Kenneth Ryan, MD, was the first in the world to describe how human ovaries produce estrogen from two types of specialized ovarian cells, laying the foundation for advances in female health.
1966: Edward Purnell, MD, pioneered the use of B scan ultrasonography to study the eye and orbit and diagnose eye and orbital diseases. In 1972 he developed the first hand-held ultrasound device for the eye.
1968: S.S.C. Yen, MD, developed the first radioimmunoassay techniques for the measurement of three important pregnancy hormones, enhancing the evaluation of maternal and infant health in pregnancy.
1969: Research by Olaf Pearson, MD, developed the role of prolactin in breast cancer and pituitary glands.
1969: The role of cholesterol in blood vessel disease was developed by William Insull, MD.
1970: Walter Maloney, MD, developed the Maloney esophageal dilator, a surgical tool for enlarging the esophageal opening, still the most widely used surgical instrument of its kind.
1970: Measurement of lung function using isotopes and computer drawings developed by Scott Inkley, MD, and James MacIntyre, MD.
1971: Angel Frame invented by UH employee Angel Martinez for care of newborns.
1972: Robert Stern, MD, developed the heparin lock, eliminating the need for continuous hookup to an intravenous line for children needing frequent IV administration of antibiotics, which eventually led to home IV therapy.
1972: Clyde Nash, MD, Richard Brown, PhD, and Albert Burstein, PhD, developed intraoperative spinal cord monitoring, dramatically improving the safety of complex spinal surgery.

1972: John Kennell, MD, and Marshall Klaus, MD, demonstrated the importance of maternal-infant bonding, leading to revolutionary changes in the care of mothers and newborn infants in hospitals throughout the western world.
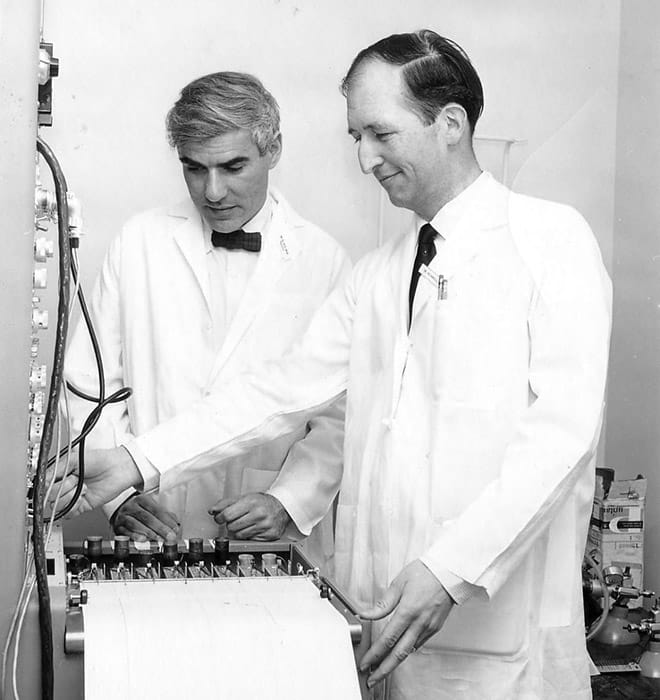

1973: John Kattwinkel, MD, Avroy Fanaroff, MD, and Marshall Klaus, MD, with David Fleming from Biomedical Engineering, developed silicone nasal prongs for the application of continuous positive airway pressure in treating respiratory distress in pre-term and near-term neonates.
1976: Beno Michel, MD, discovered a method for preserving skin tissue for use in laboratory immune system testing. Michel’s Transport Solution remains the gold standard for safely storing tissue samples during transport.
1976: John R. Haaga, MD, pioneered the use of computed tomography (CT) to guide biopsies, nerve blocks, abscess drainage and cancer treatment, significantly reducing the need for patients to have open surgery.
1978: Research technique to record accurate cardiac output was developed by Herman K. Hellerstein, MD, Anthony Bacevice, MD, and Peter Katona, MD.
1980: Irwin Merkatz, MD, conducted the first clinical trials of ritodrine, the first Food and Drug Administration-approved drug to inhibit pre-term labor, at UH MacDonald Women’s Hospital.
1980: Robert B. Daroff, MD, established the Daroff-Dell'Osso Ocular Motility Laboratory at the Louis Stokes Cleveland VA Medical Center, one of the premier Neuro-Ophthalmology research laboratories in the world.
1980: Kingsbury Heiple, MD, pioneered the improvements of artificial finger joints.
1981: Nikon Cheung, MD, and other researchers at Rainbow Babies and Children’s Hospital, pioneered work treating neuroblastoma patients with antibodies, significantly advancing the field of targeted cancer immune-therapy.
1982: Randall Marcus, MD, developed revolutionary improvements in the design of an interlocking nail system to repair fractures, particularly of the long bones, which improves the healing rate and reduces the risk of infection.
1986: Arthur Zinn, MD, Douglas Kerr, MD, Charles Hoppel, MD, published the first description and detailed characterization of a defect (in the enzyme fumarase) in the famous pathway required for energy metabolism, the Krebs cycle.
1987: Jerrold Ellner, MD, and Frederick Robbins, MD, established a memorandum of understanding with Makerere University in Uganda, linking Cleveland and Kampala AIDS research and care efforts. This linkage helped drive Uganda’s leadership response to the emerging AIDS epidemic in Africa.
1988: Herbert Meltzer, MD, conducted the first human trials of clozapine and established it as an effective medication for treatment-resistant schizophrenic patients. Clozapine remains the most effective antipsychotic agent available today.

1989: Joseph Calabrese, MD, in collaboration with researchers at Case Western Reserve University, launched groundbreaking studies that show the effectiveness of anticonvulsants and atypical antipsychotics in treating bipolar disorder.
1989: Olof Pearson, MD, and Charles Hubay, MD, pioneered the use of the drug tamoxifen for breast cancer. It is still widely used today.
1990: Anthony Maniglia, MD, was awarded the first of five patents leading to technology for developing the totally implantable cochlear implant.
1994: Huntington Willard, MD, describes Xist, the gene that is responsible for inactivation of one of two X chromosomes in females, and how it works.
1995: Cliff Megerian, MD, proved the origin of inner ear tumors in Von Hippel-Lindau disease, an inherited disease that causes tumors and cysts throughout the body; in 2002 he described the first technique to remove these tumors and preserve hearing.
1995: Michael Konstan, MD, Pamela Davis, MD, PhD, and Charles Hoppel, MD, demonstrated ibuprofen’s profound effect on slowing the loss of lung function in patients with cystic fibrosis, and later showed that twice-daily therapy with high-dose ibuprofen improves survival.
1996: Pierluigi Gambetti, MD, developed the first classification of sporadic prion diseases, now used worldwide in diagnosing this class of dementias, caused by mutation of the prion protein gene. Dr. Gambetti defined and named fatal familial insomnia and also linked the same mutation to Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease.
2000: Raymond Onders, MD, and colleagues developed an innovative diaphragmatic pacing system (DPS) that has since greatly improved the quality of life for paralyzed people and people with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS).

2001: Kumar Alagramam, PhD, identified an important gene responsible for Usher’s syndrome-related deafness, paving the way for potential new treatments.
2002: Jonathan Lass, MD, and a team led by Eric Pearlman, PhD, discovered the bacteria that in conjunction with a worm, Onchocerca volvulus, causes a disease of sub-Saharan Africa known as river blindness. Their work led to the use of antibiotics to treat this disease, a totally new approach.
2002: Pamela Davis, MD, PhD, and Michael Konstan, MD, performed the first-in-human clinical trial of a non-viral gene therapy approach in patients with cystic fibrosis using DNA nanoparticles.
2002: The reporting of an ALLHAT (Antihypertensive and Lipid-Lowering Treatment to Prevent Heart Attack Trial) study by Jackson Wright, MD, showed that thiazide-type diuretics should be considered first for drug therapy in patients with hypertension.
2003: Iris S. and Bert L. Wolstein Research Building opened, supported by a $25 million gift from the Wolsteins to UH and Case Western Reserve University.

2004: Shawn McCandless, MD, and Suzanne Cassidy, MD, reported that chronic diseases of childhood are primarily genetically determined and that most patients admitted to a children’s hospital have an underlying genetically determined condition.
2004: First in North America to successfully test and use Deep Brain Stimulation for treatment of Tourette’s syndrome
- UH was the first site to receive FDA approval to test DBS as treatment for medically refractory Tourette’s syndrome. In 2004, UH became the first in North America to successfully use DBS for treatment of Tourette’s syndrome.
- In November of 2007, a team of researchers at University Hospitals Cleveland Medical Center carried out the first randomized, double-blinded study of bilateral DBS of the thalamus for the treatment of medically refractory Tourette’s syndrome. Prior studies which suggested the efficacy of DBS in treating the disorder carried the baggage of being case studies or retrospective. This was the first completely experimentally sound paper supporting DBS for Tourette’s syndrome, despite the small sample size.
2005: Cliff Megerian, MD, developed a minimally invasive treatment for glomus jugulare tumors, a rare, non-cancerous skull bone tumor that involves the inner and middle ear.
2005: Sanford Markowitz, MD, PhD, discovered a new stool DNA test for colon cancer that became the first commercial test for colon cancer detection. It was later approved by the American Cancer Society and the FDA as an alternative to colonoscopy.
2008: Mark A. Griswold, PhD, developed parallel imaging technique for magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), which produces clearer, more accurate images in shorter time.
2009: The Brain Tumor and Neuro-Oncology Center, under the direction of Andrew Sloan, MD, pioneered a minimally invasive, MRI-guided laser system to treat previously inoperable brain tumors.
2012: Anthony Furlan, MD, published findings from a study that demonstrated that medical therapy is equivalent to interventional therapy for treating patients with PFO and stroke. The CLOSURE study was the first comparison of its kind and led to a significant decrease in interventions being done on stroke patients.
2012: Robert Findling, MD, showed the safety and efficacy of using medications such as lithium, antidepressants, and antipsychotics to treat childhood-onset psychiatric disorders, including bipolar disorder and schizophrenia.
2013: Jonathan Lass, MD, William Reinhart, MD, and Beth Ann Benetz, MA, CRA, FOPS, participated in a National Eye Institute study demonstrating that donor age is not a significant factor in the success of corneal transplantation, significantly expanding the pool of available tissue by including older donors.
2014: Anthony Wynshaw-Boris, MD, describes a new mechanism for the correction of abnormal (ring) chromosomes by converting skin cells (fibroblasts) from patients into embryonic-like induced pluripotent stem cells. In the future, this may be used for correcting chromosome defects, such as the extra chromosome that causes Down syndrome.
2014: Jackson Wright Jr., MD, PhD, authors new results from the Systolic Blood Pressure Intervention Trial (SPRINT). The study showed that maintaining a new, lower target for systolic blood pressure, the top number in a blood pressure reading, results in lower heart attack, stroke and death rates.
2015: Jonathan Miller, MD, was the first in the world to demonstrate that DBS has the potential to improve memory after traumatic brain injury.
2016: A study conducted over 30 years by Saul Genuth, MD, the late William Dahms, MD, and Rose Gubitosi-Klug, MD, PhD, demonstrated that intensive diabetes management aimed at near-normal blood glucose levels reduces an individual’s risk of diabetes-related complications and mortality.
2018: First early detection device created for esophageal cancer.
2020: First in the nation to test a COVID-19 antiviral drug and first in Ohio to offer national vaccine studies.


